Startups building on IndiaStack: A Landscaping Study

In 2010, India began an ambitious project to provide a 12-digit unique, permanent, and digitally secure identification number to its residents by securely capturing the demographic (Name, DoB, Gender, Address and Mobile No.) and biometric details (Fingerprint and Iris Scan). Under the leadership of Nandan Nilekani, a dedicated team of experts collaborated together to give shape to the Aadhaar project under the aegis of Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) and rapidly took it to scale, crossing the one-billion mark in April 2016.
Realising the digital innovation potential and the immense outreach of Aadhaar, a host of other open-source Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) were developed over the years viz.eKYC, eSign, Universal Payment Interface (UPI), DigiLocker, and Aadhaar Enabled Payment Services (AEPS). Collectively, Aadhaar, Jan Dhan bank accounts, and Mobile phone access (JAM) laid the foundation of IndiaStack.
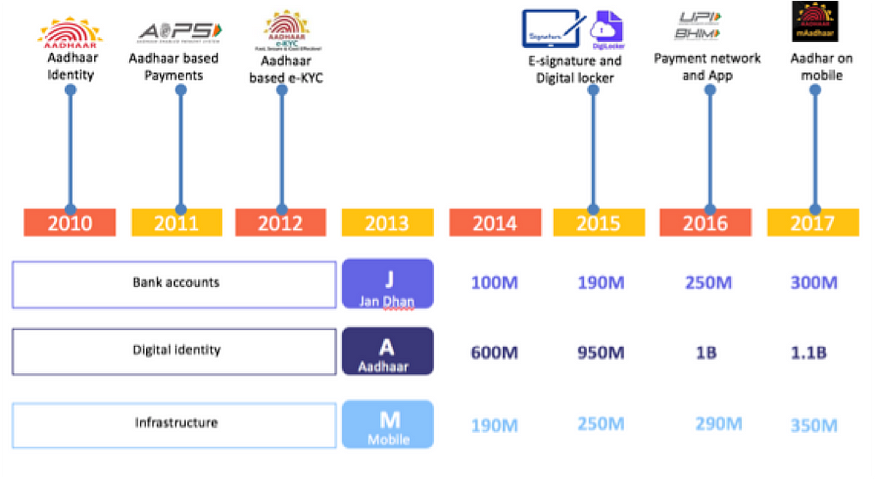
IndiaStack is a set of APIs (Aadhaar, UPI, eKYC, eSign, DigiLocker) that allows governments, businesses, startups, and developers to utilise a unique digital infrastructure to solve India’s hard problems through presence-less, paperless, and cashless service delivery. It unleashes for the government and private entities myriad possibilities for building innovative digitally-enabled solutions.
For instance, in a traditional college admission environment, a considerable amount of manual paperwork is involved. Not only does this overload the administration, it also doesn’t effectively solve the often-encountered problems of fake documents and identity misuse. By utilising IndiaStack APIs like DigiLocker, the entire system of documentation can be transferred toa presence-less and paperless Aadhaar-enabled secure digital platform, wherein documents are uploaded and authenticated by the student using eSign and the access is consensually granted to the administration department of the college, thereby improving end-to-end efficiency, convenience, and authenticity considerably.
Insights from IndiaStack Startup Ecosystem
In view of the potential of this technology platform, we studied around 150 startups using IndiaStack APIs across various sectors. Some insights from this study have been highlighted below:
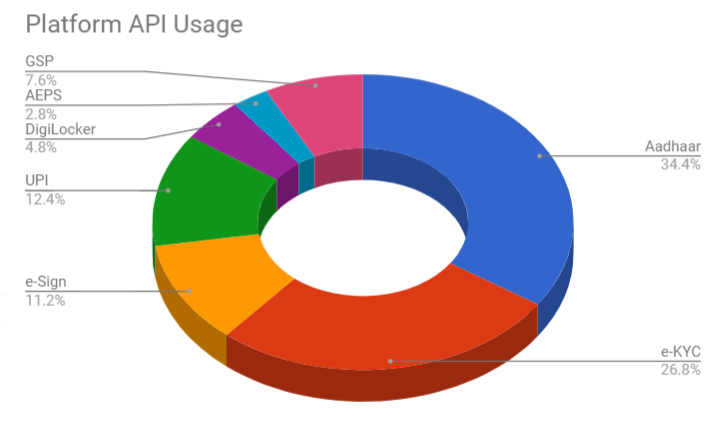
Overall, Aadhaar (60%) and eKYC (50%) made upbulk of the entire use cases. They are being increasingly adopted by a number of startups in a wide range of sectors such as paperless processing, background verification, digital lending, and tax compliance. Accessed via AUAs and KUAs, building solutions by using Aadhaar data provides credibility and agility for businesses as well as customers.
UPI, accounting for 25% of entire use cases, is gradually becoming an integral payment option in a number of payment/wallet-based services, as cashless transactions pick up traction.
DigiLocker and e-Sign, accounting for 8% and 20% of use cases, respectively, are primarily focusing on paperless documentation and ensuring authenticity. With the likes of TrueCopy and Syntizen, a larger number of government and private agencies are relying on converting their administration to a digital platform.
Primary Sectors using IndiaStack
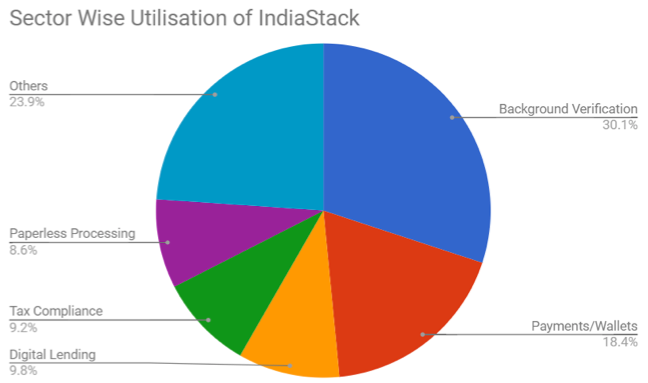
1. Background Verification
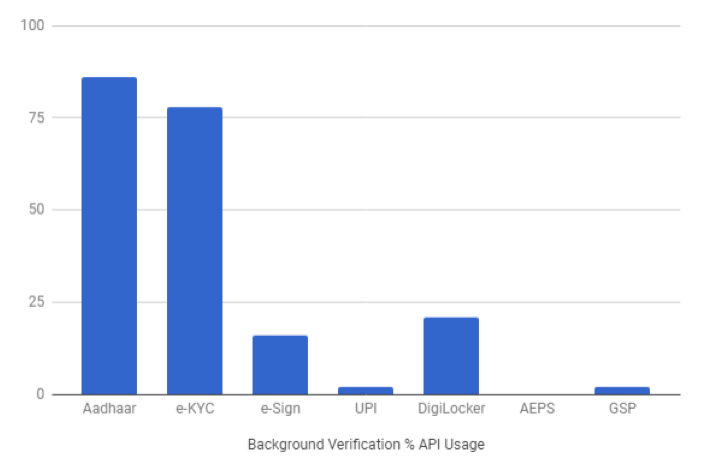
This sector includes startups which focus on employee background verification, digital identity management, eKYC and biometric based authentication. As evident in the above graph, Aadhaar and e-KYC are utilised by more than 70% of the studied startups. While startups like AuthBridge, AadhaarAPI, FRS Labs, BioEnable and Evolute focus primarily on these two APIs, others like DirectVerify, Checkwala and CertiSafe also offer DigiLocker, thereby providing document verification and digitising feature along with employee background verification.
2. Payments/Wallets
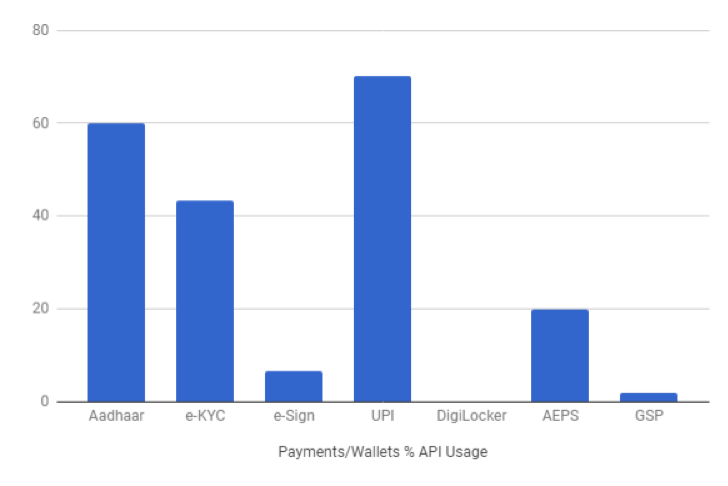
Unsurprisingly for the Payment/Wallets sector UPI is the dominant IndiaStack API used. With RBI’s KYC requirement being fulfilled by Aadhaar, all prominent FinTech companies like Paytm, PhonePe, Razorpay and Chillr are using eKYC to easily onboard customers, creating disruption in the way Indian customers access financial services and products. With financial inclusion and FinTech innovation progressing in tandem, it is imperative that this trend continues so that the disruption is truly inclusive.
3. Digital Lending
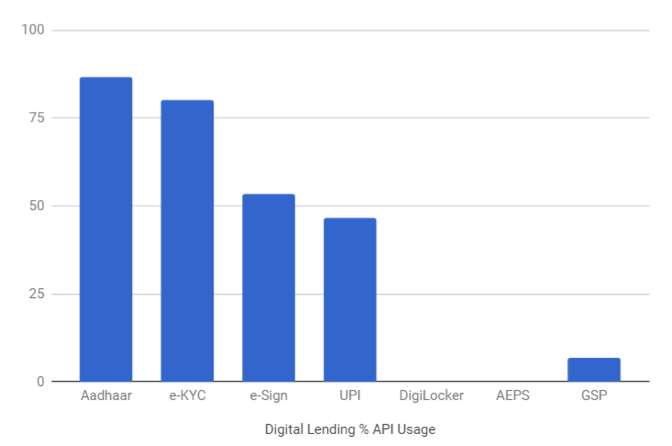
Digital lending enables borrowers (SMEs and citizens) to apply for any consumer or business lending product (loans, working capital, microcredits etc.) 24×7 conveniently via phone or web services. Startups like Capital Float, RangDe, EzCred, Indifi and CreditVidya are utilizing Aadhaar Auth and eKYC to authenticate the borrowers and then offer them quickly dispensable loans. Startups like MicroGraam, FlexLoans, NiraFinance, Quikkloan additionally utilize UPI and simplify P2P lending. With only 50% of these startups using eSign, there is still significant potential for IndiaStack to streamline this sector even further.
4. Tax Compliance
This comprises startups such as GreenGST, NaapBooks, GST Star, UnifiedGST, Easy-GST and ClearTaxwhich provide assistance in fulfilling tax obligations and submitting information to the tax authorities on time and in the required formats. Typically, these businesses are registered GST Suvidha Providers (GSP). Being cloud based, these innovative startups reduce the burden of paperwork and ease the compliance procedures for other businesses.
5. Paperless Processing
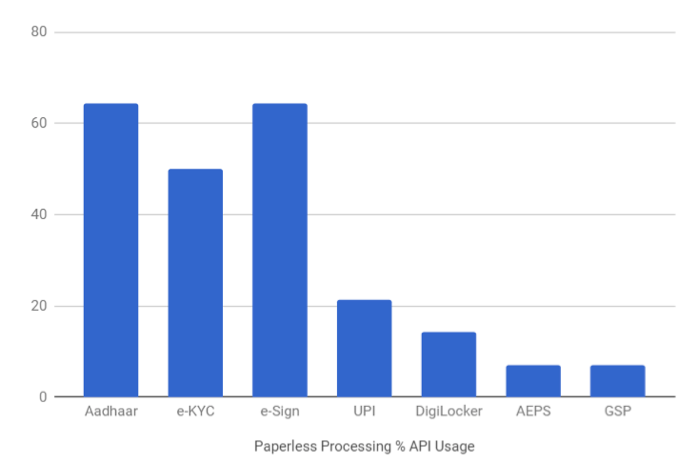
Paperless processing hosts startups which provide digital signature, electronic credentials, and documents repository platform. Using primarilyAadhaar, e-KYC and e-Sign authentication, startups like Digio, FinaHub, ezeDox, TrueCopy,Leegality and Docswallet offer online document management and DigiLocker facility.
6. Others
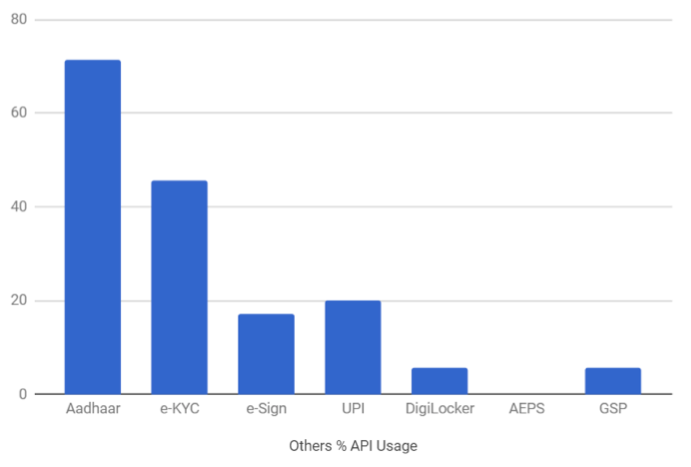
This sector includes startups belonging to upcoming sectors such as investment distribution, financial product comparison, insurance distribution, credit scoring, fraud detection and cyber security etc. Prominent players include Policybazaar, Bankbazaar, TrustID.in, Wishfin, Perfios, Acko, Indus, and Rubique. Most of the businesses utilise Aadhaar and e-KYC integration. Some, such as Reserver, Jama, Gramcover and Banknomics additionally make use of e-Sign and UPI.
Geographic Distribution of Startups
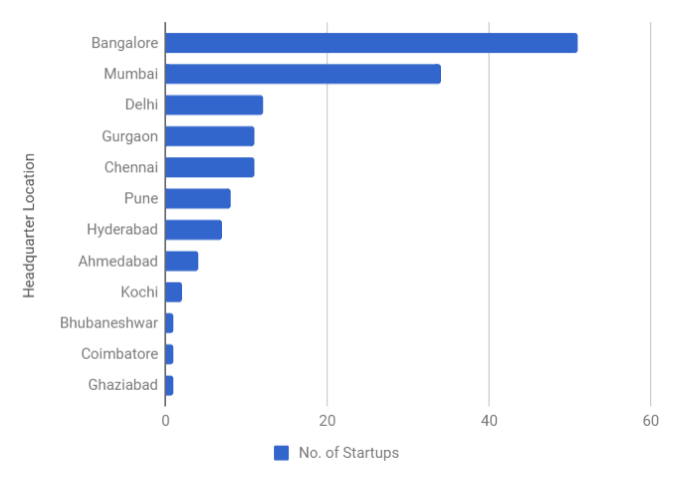
Majority of the startups in the sample have their headquarters in Bangalore, Mumbai, and NCR owing to a strong community of engineers with global work experience, savvy customers, and growing pools of early-stage capital. A high density of investors and leading industry mentors is also drawing more startups to these cities. FinTech startups find their best playground in Mumbai due convenient access to financial service providers and trade flows.
Looking Ahead
IndiaStack as a set of open access APIs is being adopted increasingly by not just FinTech startups but also various social enterprises such as RangDe and MicroGraam, which are targeting the underserved, marginalised segment. Over a billion people in India now possess Aadhaar — the single largest biometric database in the world. Half a billion have even used it digitally. Combined with other APIs such as e-Sign, UPI and DigiLocker, businesses can effectively build solutions that can potentially target big problem statements in domains of healthcare, financial inclusion, education, rural development, food security and much more.
Over 65% of the studied startups are actively using Aadhaar and more than half of them are funded by marquee VC firms and investors. The possibilities of innovating solutions for Bharat with IndiaStack appear promising and lucrative. With more advancements in technology, unambiguous regulations and supportive policies, we should see a significant increase in activity soon. With the Bharat Inclusion Initiative, the Centre of Innovation Incubation and Entrepreneurship (CIIE) at IIM-Ahmedabad will be playing a key role in ensuring that entrepreneurs building for Bharat get the much needed support as they go about their journey.